Faq
FAQ’s on Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Procedures
WHAT IS REGENERATIVE MEDICINE?
 Regenerative Medicine is therapy designed to repair and regenerate damaged musculoskeletal tissue such as tendon, ligament, cartilage and bone. Traditionally, when an injury occurs to these tissues and pain results, nonoperative pain management offers a “band aid” approach to mask pain. And when some sort of healing does occur in a ligament or tendon, it does not result in a 100% healing back to its native state.
Regenerative Medicine is therapy designed to repair and regenerate damaged musculoskeletal tissue such as tendon, ligament, cartilage and bone. Traditionally, when an injury occurs to these tissues and pain results, nonoperative pain management offers a “band aid” approach to mask pain. And when some sort of healing does occur in a ligament or tendon, it does not result in a 100% healing back to its native state.
The concept of Regenerative Medicine is to shift the paradigm of patient therapy into something that can assist with tissue repair, rather than being just a “band-aid”. Traditional therapies such as cortisone injections simply do not offer healing potential. So Regenerative Medicine uses substances that provide potential to work on the healing process for these injuries by providing building blocks known as stem cells along with growth factors and platelets that spur the body’s natural healing processes to ramp up.
WHAT IS A STEM CELL?
Stem cells are made by the body’s bone marrow and are able to differentiate into several different cell types. They are a veritable “blank slate”. They can replicate into more unspecialized stem cells, or they may react to the environment in which they are placed by receiving signals from that environment telling them which differentiation “pathway” to go down.
This may be to turn into a skin cell or muscle, cartilage, tendon, bone, red blood cell and many others. By ramping up production of the cells needed to stimulate repair, having extra supply in the area can provide the difference between an inadequate result and one that regenerates perfectly.
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT KINDS OF STEM CELLS?
There are two basic types of stem cells. The first is known as unlimited stem cells (also known asembryonic stem cells). These can turn into any kind of cell, while the second type is termed limited stem cells (also known as adult stem cells).
With unlimited stem cells, the cells have the potential to become any type of human cell. They can be replicated outside the human body and have applications for many diseases in humans.
Limited stem cells, on the other hand, do not have the same limitless diffferentiation potential and cannot be replicated outside the body. They need to be either frozen or immediately transplanted into the body.
Of note, R3 stem cell clinics do not work with embryonic stem cells, only adult stem cells. There are about ten different kinds of adult stem cells. At R3 Stem Cell Clinics, two separate kinds are utilized:
- Hematopoietic Stem Cells – these are found in human bone marrow and are able to differentiate into most cell types.
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC’s) – MSCs have been isolated from placenta, adipose tissue, lung, bone marrow and blood. They are able to differentiate into many different cell types while also assisting with the human immune response
IS REGENERATIVE MEDICINE BEING USED IN CLINICAL PRACTICE?
Yes they are. Over the past few years, multiple regenerative medicine treatments have entered clinical practice for pain management and orthopedics. These all involve adult stem cells, therefore, none are considered controversial.
The various treatment procedures being used are:
- Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy
- Amniotic Based Stem Cell Rich Injections
- Bone Marrow Derived Stem Cell Injections
- Fat Derived Stem Cell Injections
Medical Conditions that may benefit from regenerative medicine procedures include:
- Joint Arthritis
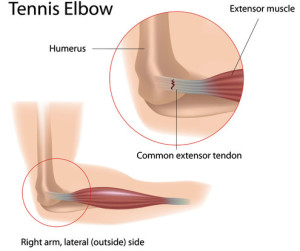
- Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow)
- Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer’s Elbow)
- Rotator Cuff Tendonitis
- Ligament Sprains
- Fractures
- Tendon injuries
- Cartilage defects
- COPD
- Kidney Failure
- Stroke
- MS, ALS
- Dementia
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Heart Failure
- Diabetes
- Diabetic Neuropathy
HAS RESEARCH PROVEN THE EFFECTIVENESS OF STEM CELLS IN MUSCULOSKELETAL MEDICINE?
There has been no definitive proof for musculoskeletal conditions with large studies. There have been small studies in both animals and humans displaying the effectiveness of the various regenerative medicine procedures, which are described on the individual Stem Cell Therapies pages.
DOES INSURANCE COVER REGENERATIVE MEDICINE PROCEDURES?
Insurance does not currently cover regenerative medicine procedures for the most part. There are certain instances in surgery where there are codes for the various procedures. But by and large, the procedures are considered a fee for service.
With the R3 Stem Cell Clinics that offer the research protocols, treatment is industry subsidized and cost approximately 40% less than otherwise.
HOW MUCH DO REGENERATIVE MEDICINE PROCEDURES COST?
There is a broad range of pricing for regenerative medicine procedures. They start at approximately $1000 and go up to $8000 per injection procedure.
WHAT TYPES OF DOCTORS OFFER REGENERATIVE MEDICINE PROCEDURES FOR MUSCULOSKELETAL CONDITIONS?
The doctors offering stem cell injection procedures come from numerous specialties, including sports medicine, orthopaedic surgery and pain management.
DO PATIENTS HAVE TO BE ACCEPTED IN A RESEARCH STUDY TO RECEIVE STEM CELL PROCEDURES?
Not necessarily. Patients may still benefit from regenerative medicine procedures even if they do not fit the inclusion criteria for one of the research studies.